According to Polaris Market Research1, the global Smart TV market was valued at USD 207.40 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 495.06 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.2%. This rapid expansion reflects the increasing demand for connected home entertainment, driven by advancements in streaming services, content integration, and AI-powered personalization.
As Smart TVs become more sophisticated, the demand for specialized app development grows. However, creating seamless and engaging Smart TV applications presents unique challenges for developers. Our Smart TV app development tutorial explores these challenges in detail and demonstrates how our expertise helps clients enhance user experiences, gain a competitive edge, and drive business growth.
Dealing with Smart TV platform fragmentation
Unlike the mobile app market, where iOS and Android dominate nearly 100% of the global share, the Smart TV ecosystem remains highly fragmented, with multiple operating systems competing for market presence.
According to Grand View Research2, Android TV continues to lead due to its open ecosystem, seamless compatibility with a wide range of applications, and integration with the Google Play Store, allowing users access to an extensive library of apps, games, and streaming services. Its familiar interface makes it a natural choice for those already using Android devices. With availability across various price segments, Android TV caters to diverse consumer needs, reinforcing its market dominance.
Roku, meanwhile, is experiencing rapid growth, driven by its user-friendly, intuitive interface and strong compatibility with major streaming services. As the same study by Grand View Research highlights, Roku’s straightforward design and simplified remote control make it particularly appealing to non-tech-savvy consumers. With streaming becoming the primary mode of content consumption, Roku’s affordability and accessibility give it a competitive edge. Strategic partnerships with manufacturers have further expanded its presence, solidifying its role in the Smart TV industry.
However, Smart TV viewers are rarely tied to a single device, often switching between multiple platforms throughout the day. To provide seamless experiences, content distributors must develop Smart TV apps that function efficiently across various devices, including set-top boxes (STBs) and , in addition to Roku and Android TV, also platforms like Apple TV, Amazon Fire TV, and Google Chromecast.
To help your customers better target their resources towards specific brands, expand the viewership, and increase ROI, thoroughly analyze the Smart TV market, define a matrix of the preferable Smart TV and set-top box platforms, and build a future app compatible with these platforms.
Also, different devices mean different SDKs and APIs that are frequently updated by vendors. To avoid compatibility problems in this regard, scrutinize the documentation for every particular Smart TV platform, strictly follow the required guidelines when deploying the app, and provide comprehensive API update support.
Besides Smart TV device diversity, things are complicated further with new operating systems constantly entering the market. The problem is that new versions are not always compatible with older TV hardware, which might lead to the Smart TV app not supporting new features.
To solve this challenge, define a matrix of the necessary OSes, test the feasibility of supporting extremely old televisions, and add custom code to make the Smart TV app backwards compatible with legacy TV hardware.

Matrix of TV platforms and OSes
What to consider for great usability and UX
TV differs a lot from smaller screens, so Smart TV app development has its peculiarities when it comes to UI and UX.
Must-have features to comply with app store standards
Optimal usage of CSS style libraries
To enable smooth watching from a 3-4 meter distance, which is typical for TVs, you have to get into the ins and outs of CSS style libraries and implement them optimally. Also, TV screens differ from mobile and desktop displays — they often have higher contrast, backlight bleeding issues, and motion blur. To address this, pay particular attention to color usage — avoiding pure black and white — and accurately distributing content across the screen to reduce strain on the eyes.
Font size is another tricky thing: it should be legible from both short and long distances while maintaining proper line spacing and weight to prevent visual fatigue. Additionally, ensure scalability across different screen resolutions (HD, Full HD, 4K, and 8K) to prevent layout shifts.
Intuitive in-app navigation
Ensuring frictionless navigation is another must. In Smart TV development, this usually means avoiding drop-down menus, prioritizing lists and smooth transitions between pages, and building an intuitive back button. Since TVs rely on remote controls, navigation should be structured so that even first-time users can intuitively move across the interface.
To streamline user interactions, consider:
- Minimizing unnecessary clicks to complete key actions.
- Implementing a grid-based layout that allows simple left-right navigation rather than complex scrolling.
- Using clear, visible indicators to highlight active selections.
Also, gesture-based navigation and voice control integration are becoming increasingly relevant for Smart TVs. Supporting these features can improve accessibility and expand your user base.
Transparent focus state development
A focus state is a crucial UI element that helps TV viewers understand where they are while navigating through a Smart TV app. Unlike smartphones or tablets, where users tap directly on the screen, Smart TV apps rely on directional input from remotes. This makes it essential to design a clear and visually distinct focus indicator that doesn’t blend in with surrounding elements.
Key focus state best practices include:
- Avoiding the same colors for the focus highlight and other UI components.
- Using animations or subtle glows instead of harsh outlines for better visibility.
- Ensuring focus consistency across the entire app, even when transitioning between pages.
Additionally, responsive focus management should be implemented for accessibility — keyboard and voice-controlled navigation should work seamlessly alongside traditional remote-based navigation.
UX features to engage TV viewers
Smart TV app development might include a lot of customized features such as voice-powered control or a custom keyboard with auto-complete functionality. This presupposes additional research, effort, and money, which should be thoroughly discussed during the requirements elaboration. Some of the features that TV viewers would expect from Smart TV applications may include the following ones:
Personalized content search
In the time of user-driven OTT, enabling the personalized discoverability of content is what can give viewers the videos they would like to watch without scrolling through the full library.
Voice search & AI-powered navigation
With the evolution of user habits, TV device manufacturers have standardized voice control in newer models. If you choose to enable voice search, integrating Alexa, Google Assistant, Siri, or Amazon Echo is a must. Additionally, AI-powered navigation allows users to interact with apps more intuitively — understanding contextual commands rather than relying on strict keyword inputs.
Synchronized usage across multiple platforms
Users increasingly expect their Smart TV app experience to be seamlessly connected with other devices they use daily. Some examples include:
- Cross-device viewing allows users to pause on a Smart TV and resume on mobile or tablet.
- Parental controls enable restriction settings that sync across TV, mobile, and web apps.
- Cloud-synced preferences that keep watchlists, recommendations, and settings unified across all platforms.
Gesture & motion-based controls
With the growing adoption of gesture-based technology, some Smart TV models now support hand gestures and motion tracking for interaction. While still an emerging trend, Smart TV apps that leverage gesture control (e.g., wave to scroll, pinch to zoom) can provide a touchless and more immersive experience.
Multi-user profiles & AI-driven UI adaptation
Smart TVs are often shared devices within a household. Offering multi-user profiles ensures personalized recommendations, content preferences, and UI layouts for each user. Additionally, AI-driven UI adaptation can dynamically adjust layouts, font sizes, and accessibility features based on individual usage habits.
Real-time interactive features
Smart TVs are evolving beyond passive viewing, with more interactive and community-driven experiences. Some advanced engagement options include:
- Live polls & audience participation used in streaming events, sports, and game shows.
- Real-time chat & social media integration, allowing users to engage with live content while watching.
- Second-screen experiences, syncing mobile apps with TV content to provide extra information or interactive overlays.
Low-latency streaming & 8K optimization
With 8K content becoming more mainstream, Smart TV apps must be optimized for ultra-high-resolution streaming while ensuring low latency. Implementing adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR), efficient compression algorithms, and cloud-based CDN integration will be crucial for a buffer-free experience.
How we can serve your needs
Why not add interactivity to your OTT platforms and boost TV viewer engagement? Let your users feel special by giving them a personalized user experience.
How to deal with digital rights management
When a business develops a Smart TV app for webOS and Tizen, ensuring compatibility with streaming techniques and DRM systems is crucial. While modern Samsung and LG TVs support MPEG-DASH, HLS, PlayReady, and Widevine DRM, older models may have limitations.
For example, webOS TV 5.0 and higher support HTTP/2, but not HTTP/3, while Widevine Classic has been deprecated starting from webOS TV 23. Similarly, Tizen OS continues to support PlayReady and Widevine, making it essential to configure streaming settings properly.
If your app encounters playback issues due to DRM incompatibility, consider these two solutions:
- Modify the streaming configuration: Ensure that your DRM system is supported on the target devices. If using Widevine Classic, switch to Widevine Modular for webOS TV 23 and later.
- Implement a multi-DRM strategy: Use a flexible DRM approach that supports both PlayReady and Widevine, ensuring a broader reach across Smart TVs.
By applying these strategies, you can provide a seamless streaming experience for users while maintaining compliance with DRM requirements.
How to avoid rejections when submitting Smart TV apps to app stores
Smart TV solution approval in an app store can take a long time — about 2-3 months, depending on the version. If you don’t go into details about the solution approval process and its tricky cases, you may get your Smart TV app rejected.
For submission, Smart TV app developers need to provide an app store with a complete application map describing its functional capabilities, navigation scenarios, and other UX components. The next stage includes a substantial test checklist and test execution as per it for an app to go through an approval process. Frequently, some of the must-have points are missed, which leads to rejections. To eliminate the “rejected” status and not get into a vicious circle, it’s vital to strictly follow the checklist to get your Smart TV app submitted and approved by the app store.
How to develop a Smart TV app with a solid performance
One of the reasons for app store rejection might be a poor video streaming speed. If you want to avoid re-submitting the app and postponing the market release, enhance the solution performance.
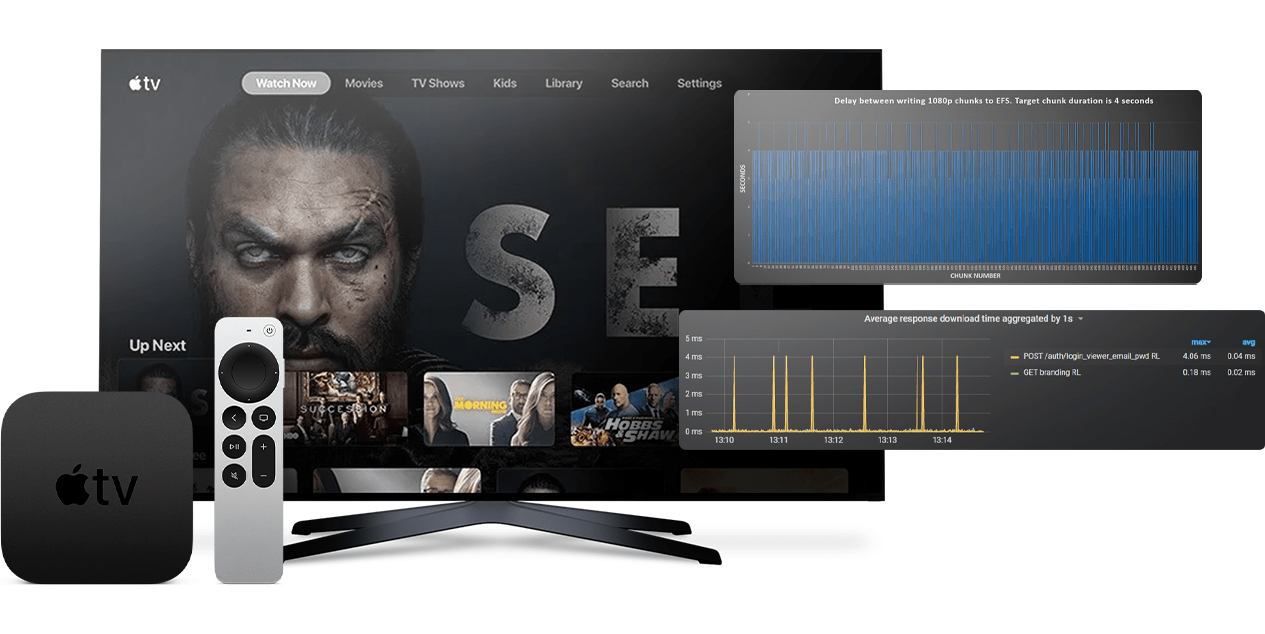
Smart TV performance
When handling multiple platform versions, it’s key to timely switch off the functionality that isn’t supported on older versions. Simplifying UI is another way to significantly improve frontend performance. This can be done by using React renderers with canvas instead of HTML DOM elements and by omitting complicated CSS styles like shadows or 3D. However, canvas isn’t applicable for older TVs, as it will reduce the Smart TV app’s performance and rendering.
Considering the fact that TV is a low-memory device, and its characteristics differ from that of PCs, pay particular attention to performance profiling. This will help detect TV’s memory errors, CPU limitation, uninitialized memory, as well as the improper allocation or deallocation of memory.
We also recommend writing custom code for Smart TV apps with backend performance in mind, implementing CDN set-ups, and conducting highly-performant automated Smart TV testing. To deal with hardware performance challenges, you should optimize the app for older TVs when needed and implement graceful degradation. Sharing one codebase logic for scaling to multiple platforms may be viable for Smart TV development projects with several devices in mind. This allows using a single code architecture as the core, saving on the project costs and customizing specific needs for each platform.
Case in point: Modular OTT app with a single codebase for 13 platforms and 25 devices
Find out how Oxagile created an easily configurable frontend OTT solution with further adaptations for various telcos in mind. The team designed the solution architecture allowing for a massive code reuse.

Smart TV app: Solving QA problems
Smart TV testing is a complex process that presupposes a great volume of work due to TV device fragmentation.
To deal with this efficiently, define a matrix of platforms for testing as well as test the feasibility of using real-life devices. As practice shows, real-life devices are key to testing particular features like video streams or custom navigation. For the rest of the scenarios, emulators come in handy. Moreover, TVs are not apt to screenshot testing, and with emulators you can get screenshots through a host OS.
Among other methods you can use to speed up the QA processes are:
- Automated parallel testing across various emulators
- Avoiding sending large messages (over 1,000 symbols) via WebSockets
- Dividing large messages into several smaller ones
When testing on TV devices, debug connections might be lost due to high loads. With this in mind, capitalize on real-life devices only to test the functionality that can’t be tested on emulators and timely restart the debugging process.
Smart TV development projects typically combine both manual and automated testing. Though the latter is considered to be more expensive due to the technologies involved, it will pay off in the future. Compared to native TV app development, it saves the project time and makes it faster and easier to debug even “invisible” bugs.
Conclusion
Smart TV sales are only increasing. And although major players are leading the market, you can always join the competition and find your niche. Being in the loop about our recommendations on platform fragmentation, performance, and UI, you’ll be able to expand your client base.
Sources:
1. Polaris Market Research, Smart TV Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
2. Grand View Research: Smart TV Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report